Electric Arc Furnace Steel: What It Is and Why It Matters
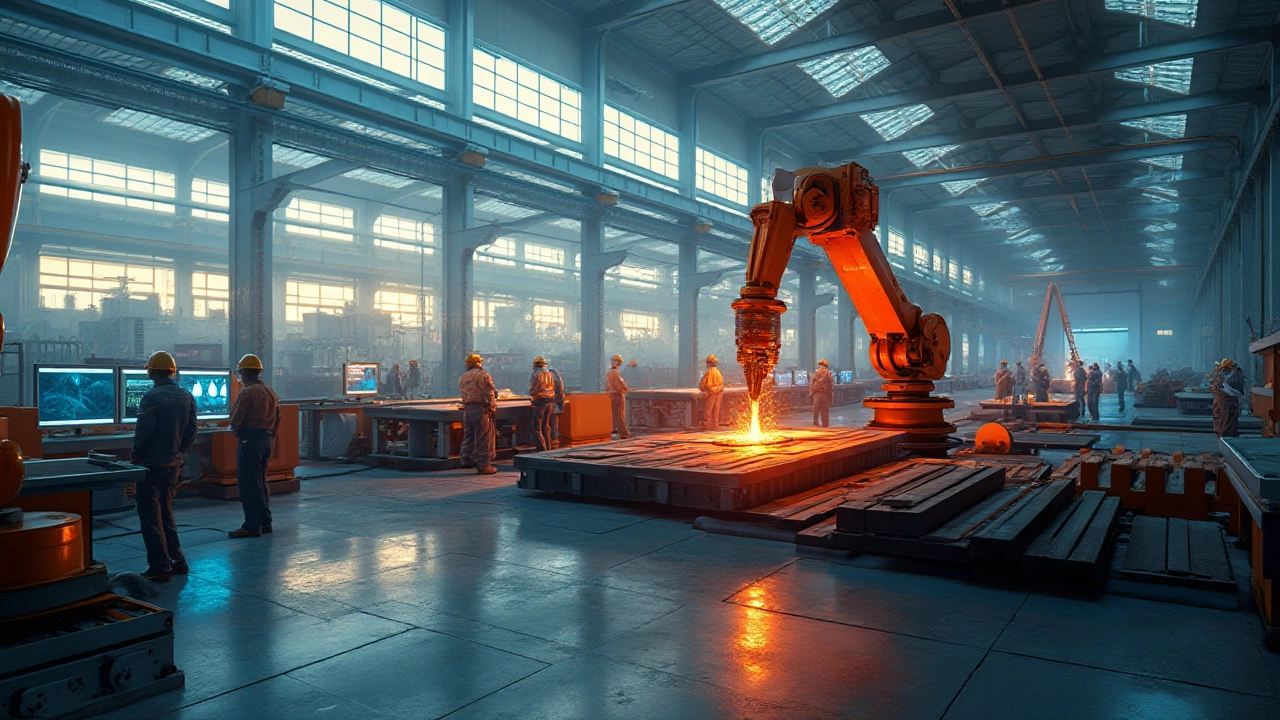
When talking about electric arc furnace steel, steel made in an electric arc furnace (EAF), a process that melts scrap or direct‑reduced iron using electric arcs. Also known as EAF steel, it offers quicker cycles and lower carbon footprints compared with traditional blast furnace methods. electric arc furnace steel is reshaping how manufacturers meet demand while cutting emissions.
Another key player is steelmaking, the broader set of processes that turn raw iron into finished steel. Within steelmaking, the electric arc furnace uses powerful electrical currents to generate heat, allowing precise control over composition and temperature is the core technology. This equipment can switch between scrap and virgin feedstock, making it versatile for automotive, construction, and appliance sectors.
In India, the rise of sustainable manufacturing practices that lower waste, reduce energy use, and minimize greenhouse gases has pushed steel producers toward EAF solutions. Companies are betting that greener steel will attract both domestic buyers and export markets, especially as regulations tighten and consumers demand lower‑carbon products. The shift also ties into the broader push for circular economy models, where scrap steel becomes a valuable resource rather than waste.
How the Technology Impacts Jobs, Costs, and the Environment
Adopting EAF technology changes the labor landscape. Operators need electrical engineering skills, while traditional blast furnace roles focus on coke handling and furnace maintenance. This transition opens up higher‑paid, technically focused factory jobs—something we saw highlighted in articles about top-paying manufacturing roles. Costs shift as well: electricity becomes the main input, so plant locations near cheap power grids gain an edge.
From an environmental standpoint, the carbon intensity of EAF steel drops roughly 30‑40% compared with classic methods, especially when the grid incorporates renewable energy. That reduction aligns with India’s climate goals and with global trends where steelmakers pledge net‑zero targets by 2050. The lower emissions also mean fewer pollutants in surrounding communities, improving public health and workplace safety.
Beyond the plant floor, the steel sector influences the wider economy. Manufacturing hubs that embrace EAF see ripple effects—new logistics services, material suppliers, and downstream fabricators all benefit. This chain reaction boosts local economies, creates ancillary jobs, and drives innovation in related fields like advanced alloys and high‑strength coatings.
Readers will soon find articles that dive deeper into each of these angles: a look at India’s top steel‑producing states, a comparison of global steel quality, insights on the fastest‑growing manufacturing careers, and practical tips for companies aiming to shift to electric arc furnace operations. The collection below brings together expert analysis, real‑world case studies, and actionable guidance that together paint a full picture of where electric arc furnace steel stands today and where it’s headed tomorrow.
US Steel Mills in 2025: Which Ones Are Still Operating?
Discover how many steel mills remain in the US, the types still operating, major owners, recent closures, and what the future holds for American steel production.
- manufacturing
- India
- food processing
- garden tips
- rice cultivation
- government schemes
- balcony garden
- urban gardening
- balcony gardening
- profitable business
- business ideas
- plastic manufacturing
- drip irrigation
- plant care
- steel manufacturing
- sustainable gardening
- startup ideas
- steel industry
- flower gardening
- textile manufacturers